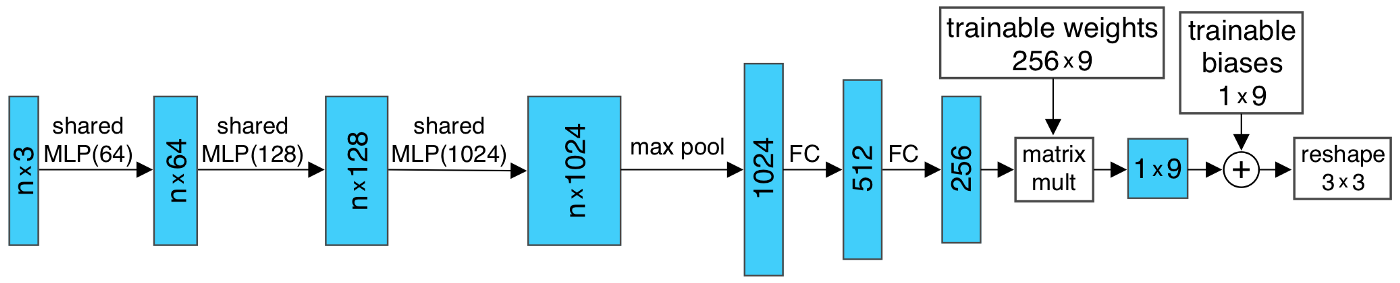
PointNet的输入是一个点集,这个点集可能表示某个场景下的某个物体,那么PointNet应该具备以下几个特点:
- 点集的置换不变性:改变点的输入顺序,不影响输出结果。比如不论输入是,还是。模型应该将点集所表示的物体预测成同一类。
A network that consumes N 3D points needs to be invariant to N! permutations of the input set in data feeding order.
- 点集的刚体变换不变性:对所有点做同一rigid transformation(R/T),模型的预测结果不变。
As a geometric object, the learned representation of the point set should be invariant to certain transformations. For example, rotating and translating points all together should not modify the global point cloud category nor the segmentation of the points.
为了满足上述两个特点,PointNet做了下面两点结构设计:
- 对无序点集具有置换不变性的对称函数

其中h函数就是Figure 3.2的 shared MLP,g函数是Max Pooling操作。 - 用于表示刚体变换的T-Net
PointNet++的核心组成主要包括上图左半部分的set abstraction和右半部分的feature propogation:
- Set Abstraction Level
- Sampling Layer:使用Iterative Farthest Point Sampling(FPS)进行采样,从而确定每个group的中心点。
- Group Layer:在group的中心点的基础上,选取candidate point形成一个group,这个group的点云数据作为PointNet的输入。
- PointNet Layer:这层没啥可说的,就是上面PointNet这节的内容。
- Feature Propogation Level
- Interpolation Layer
We use inverse distance weighted average based on K-nearest neighbors(as in Eq.4.2 in default we use p=2, k=3). The interpolated features on points are then concatenated with skip-linked point features from the set abstraction level.
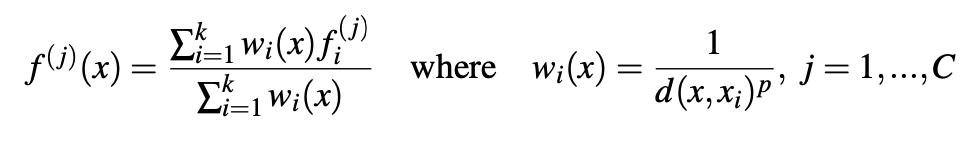
- Unit PointNet Layer
Then the concatenated features are passed through a "unit pointnet", which is similar to one-by-one convolution in CNNs.
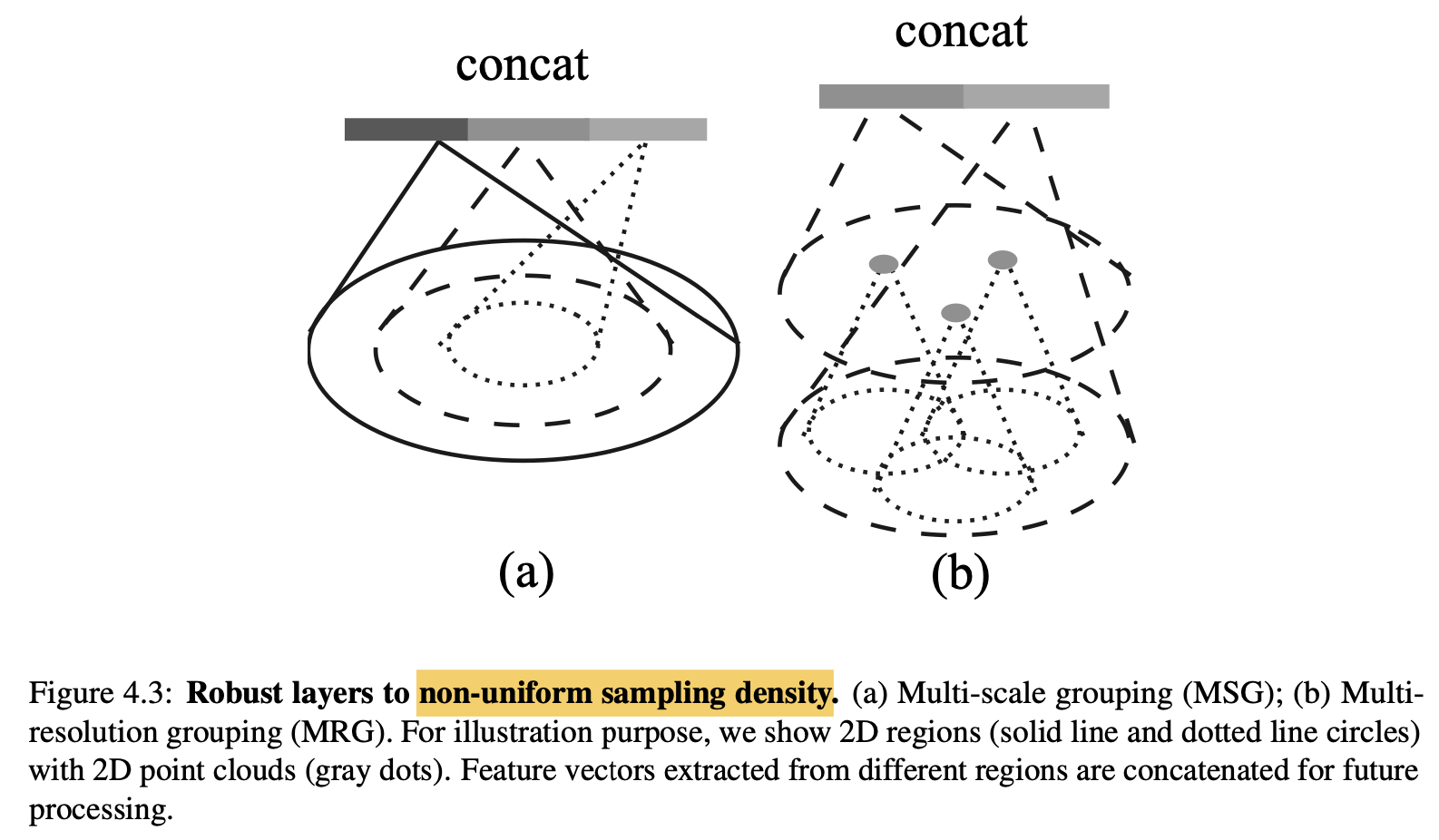
点云数据有一个很显著的特点——在不同区域点云的密度不一样。比如通过Lidar采集的点云数据,通常距离较远地方的点云较稀疏。这种分布不均的特性给点云的特征学习带了了很大的挑战,PointNet++对PointNet Layer做了改进,提出两种density adaptive PointNet Layer——Multi-Scale Grouping(MSG)和Multi-Resolution Groupint(MRG)。
我们知道2D的BBox可以用参数来描述,3D BBox需要更多的参数进行描述:
The 3D box is parameterized by its size , center , and orientation relative to a predefined canonical pose for each category. In our implementation, we only consider the heading angle q around the up-axis for orientation.
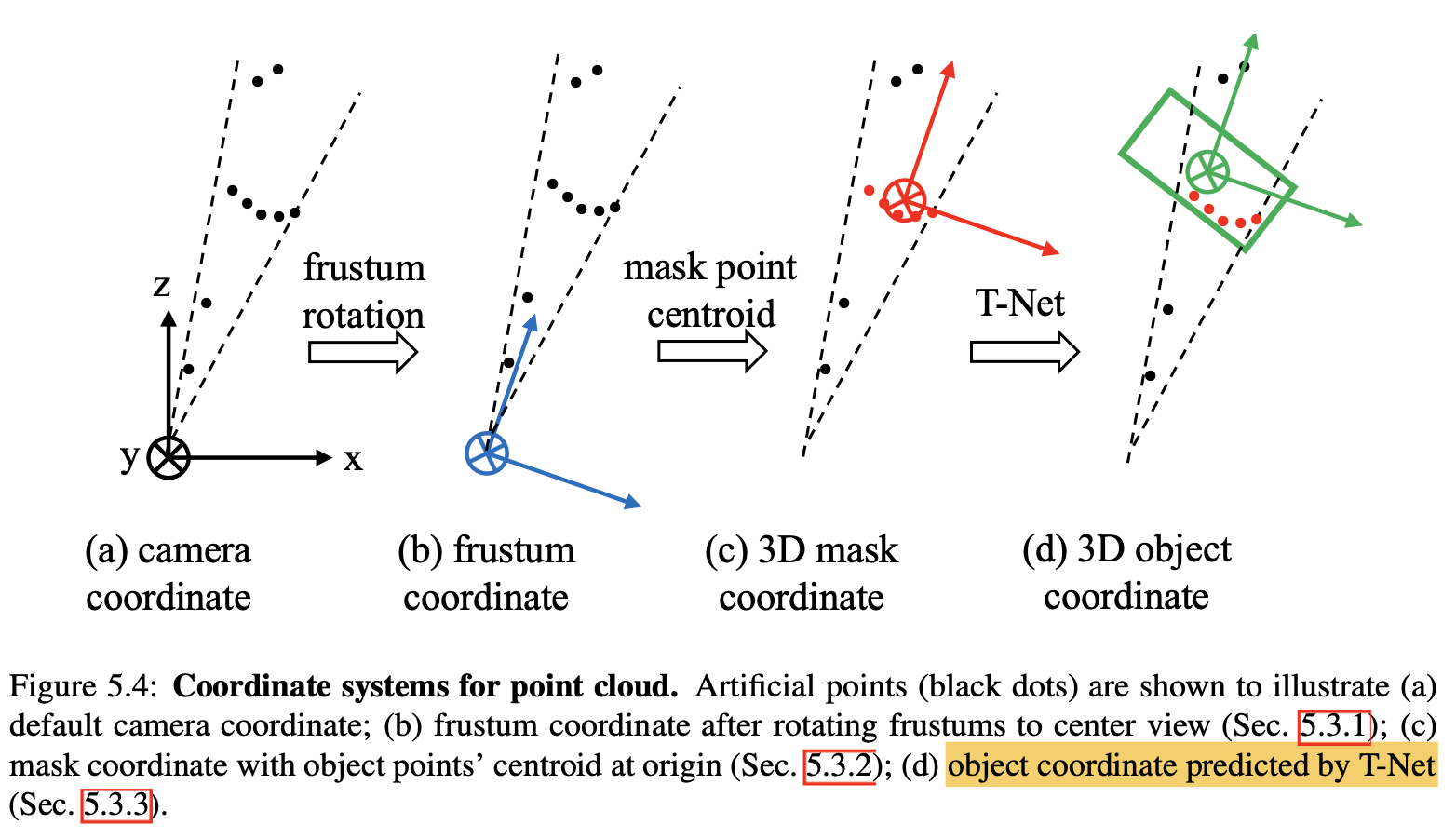
对上面这张图,需要做以下几点的解释说明:
- 上面涉及到了frustum coordinate,mask coordinate和object coordinate三个坐标系,它们之间的变换可以用下图表示。
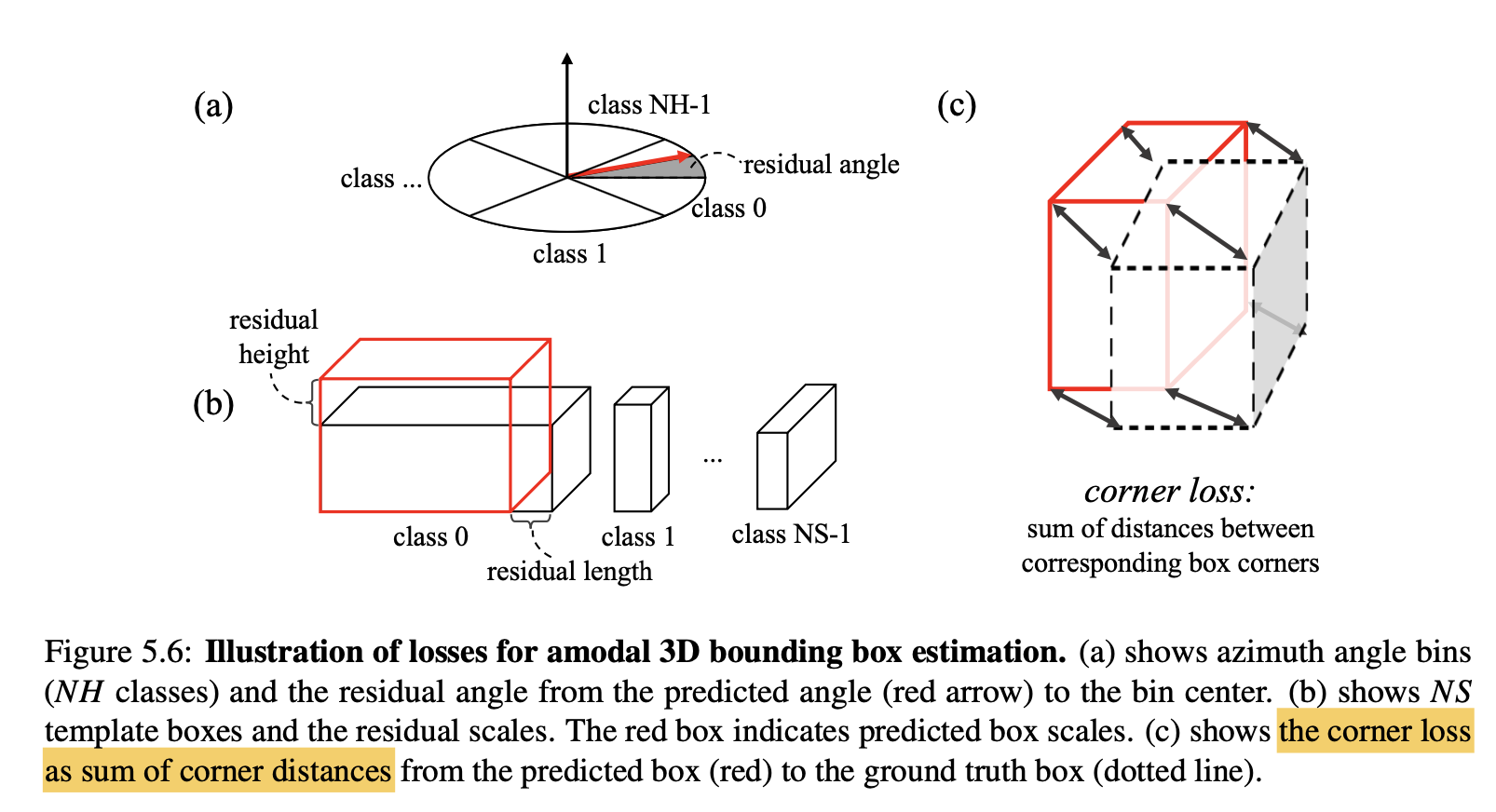
- Amodel 3D Box Estimation PointNet输出的位数为。Frustum PointNet定义了NS个尺寸模板,并将heading angle 均匀的划分成了NH个angle bins。模型会预测:1)尺寸和heading anlge属于哪个模板(NH+NS位);2)的residual(3NS + NH位);3)中心点在object coordinate下的resiudal(3位)。
- 对于中心点的预测,论文描述地非常明白
主要包含以下任务的损失:
- 是3D Instance Segmentation PointNet的损失函数。
- 和是和中心点相关的损失,前一个是T-Net的回归损失,后一个是Amodal 3D Box Estimation PointNet的回归损失。
- 是heading angle的模板分类损失,是heading angle residual的回归损失。
- 是3D BBox尺寸的模板分类损失,是尺寸的回归损失。
-
In essence, the corner loss is the sum of the distances between the eight corners of a predicted box and aground truth box. Since corner positions are jointly determined by center, size and heading, the corner loss is able to regularize the multi-task training for those parameter
版权声明:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若内容造成侵权、违法违规、事实不符,请将相关资料发送至xkadmin@xkablog.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即处理!
转载请注明出处,原文链接:https://www.xkablog.com/cjjbc/48389.html
