一、Software Crisis
(1)定义:在计算机软件开发和维护中遇到的一系列严重问题
(2)原因:
·技术:软件size变大,复杂性增加
·管理:缺少理论领导;太依赖个人能力和创造性;未充分理解用户需求
(3)表现(Menifestations)
·成本高;质量低;代码难维护;周期长;开发过程难控制、难管理;
(4)解决:
减少:1.充分理解计算机软件
2.在developing software推广成功的techniques,methods和tools
3.消除misunderstanins和practices
4.对时间人和资源采取更合理的管理方法
消除:Software Engineering
二、Software Engineering
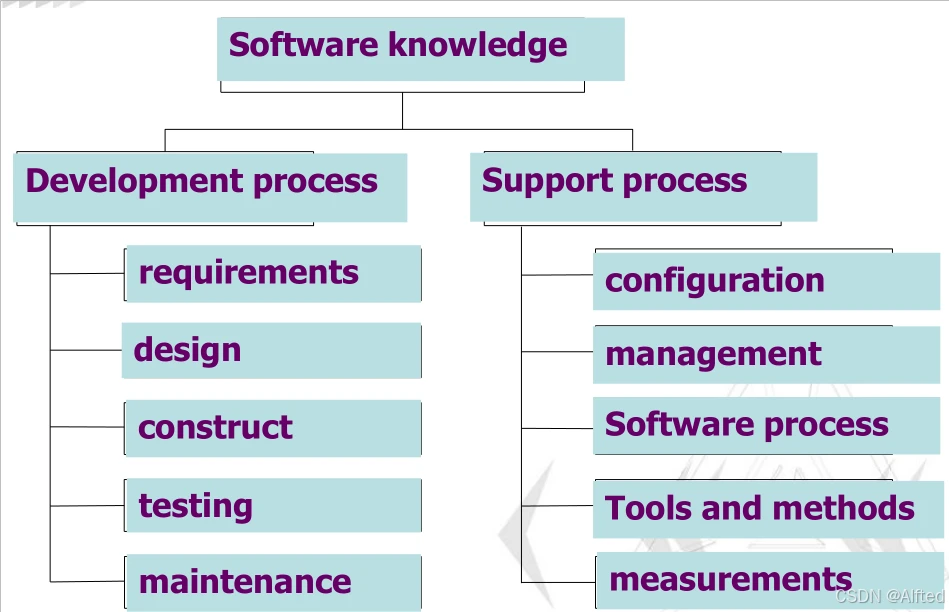
(1)、Unified Modeling Language(UML)
1.一种语言或工具,而不是一种方法;含components的representations和connection
2.function:Visualization,Specification,Constructing和Documenting
(2)elements:methonds, tools, process
1.methos:"how to do it";传统的和面向对象的
a.传统:strutured methods;static idea;将process分成phases去完成任务;缺少灵活应变能力;
b.面向对象:对象是unified software,结合了data和operational behavior;所有对象被分成类,类有数据和operations(data:Static,Operation:dynamic);根据父子关系把相关的弄到一个layered系统中;下层有上层数据和操作称为继承;对象只在传输数据关联称为封装
2.tools:"what to do with what",自动或半自动环境
3.process:"how to control, coordinate and assure quality",框架为了实现高质量软件定义每个任务步骤
三、software development life cycle(SDLC)
(1).international standard ISO/ISE 12207定义了该概念
(2)life cycle:软件开发的macro(宏观)框架;分为Sequential、iterative、incremental、agile;
·包含定义、开发和维持
(3)可行性分析:technical,economical,social
(4)传统life cycle model
1.waterfall model(seeks to complete system at once)
·适用:嵌入式系统,必须与硬件连接交互;规格说明和设计文档完整+安全问题;大软件+有相似模型
·缺点:change发现越晚cost越高;假设太多导致理想化;文件驱动/计划驱动
2.prototyping model
·适用:UI;检查设计可行性
·缺点:实际项目中开发技巧和工具用不到;不断修改;先前版本会丢弃;最终也不一定用;为了成本降低进度提高,会丢弃一些功能(响应时间、利用率等),导致质量低
3.incremental model(逐步增加功能)
·第一个增量要是最核心的功能
·计划驱动中增量是提前定的;敏捷中早期是定的
·缺点:过程不可见;不断修改代码导致error
(5)Spiral Model:用原型和其他方法最小化风险;适合大而复杂的系统
(6)Fountain Model:
·迭代;面向对象;seamless(无缝);线性过程避免disorder
(7)Agile Software Development
1.迭代地传递;开发团队和用户反馈驱动;不断integration;开发团队自我管理
2.Manifestos(宣言):

3.增量style----batch delivery
4.Iterative style
5.优点:高精确度;高质量(test-driven);高速;投资回报丰厚;有效的团队自我管理
6.适用:中小型;需求频繁变化;强调role of team; centralized开发模型
(8)Extreme Programming(XP)(Agile)
1.减少需求变化成本
2.Pair-programming
3.embrace changes
(9)SCRUM process (Agile)
1.分成好多sprint cycles;
2.role
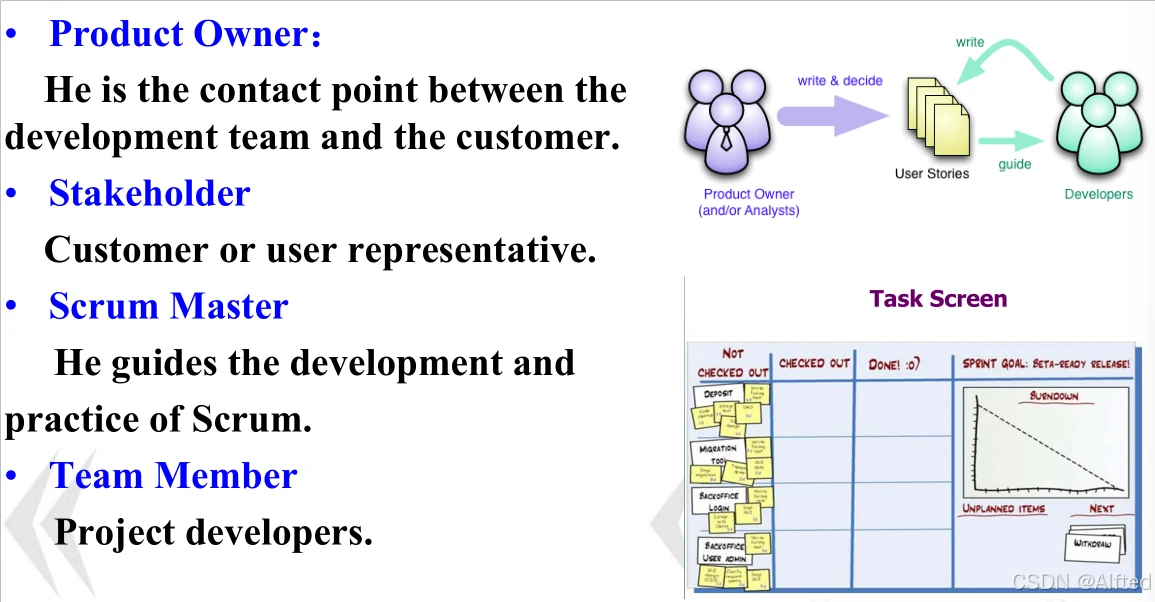
(10)DevOps Process(Agile)
1.强调宣言中“individuals and interactions are better than process and tools”
2.强调workflow一样时, development, operations and maintenance一定一起工作
3.自动,可持续传递
四、需求分析
(1)困难:不合逻辑的软件开发;开发者了解知道task area; 用脑子分析任务;视角局部;难预测影响因素
(2)可行性分析评估初始开发成本:user(business)需求(customer-driven); system需求(开发者驱动)
·系统需求是用户需求的refinement和improvement
·The reading object of the system requirements is the developer, while that of the user requirements is the client.
(3)Stakeholder
·定义:和目标系统有关的所有东西
(4)系统目标

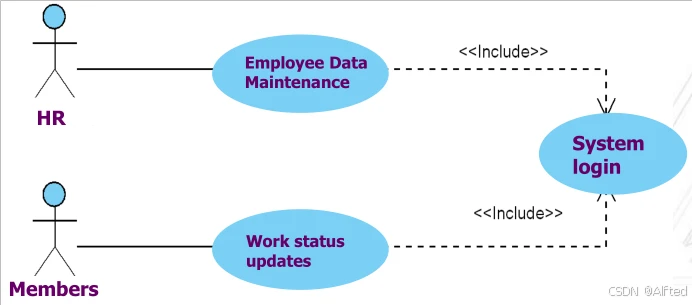
(5)Use cases(Object)
1.Actor:Role;小人符号;Object
2.Include:accomplish specific tasks, avoiding simple logical function decompositions.前面运行后后者也要一同运行
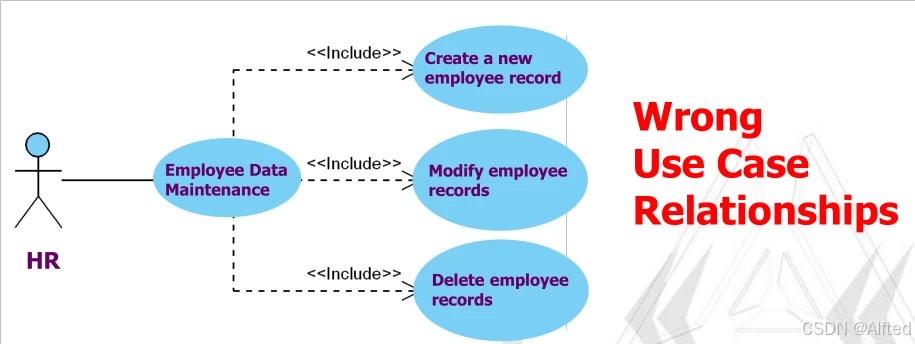
3.extend:emphasize the need for a strong expression of customer in certain situations, such as the special cases handling. 在一定条件下发生,不一定每次都会

(6)Process/Stream Modeling
1.
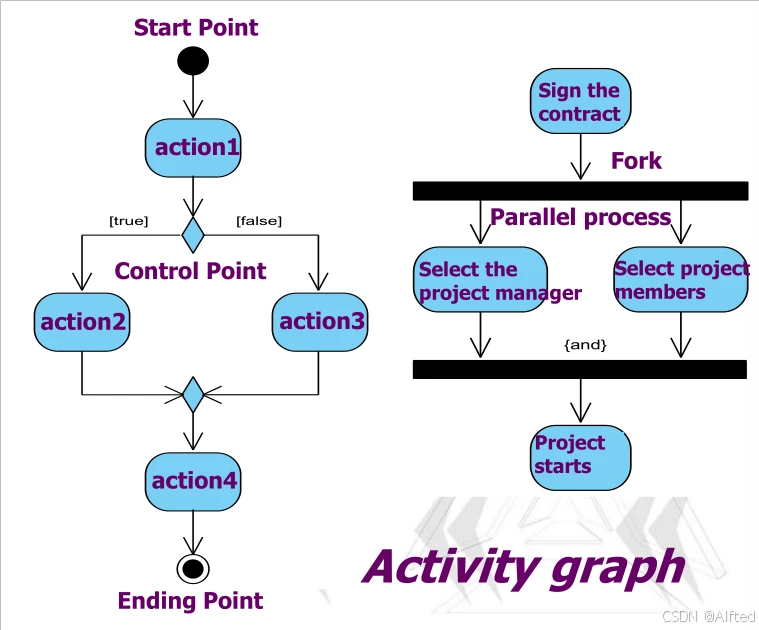
2.有object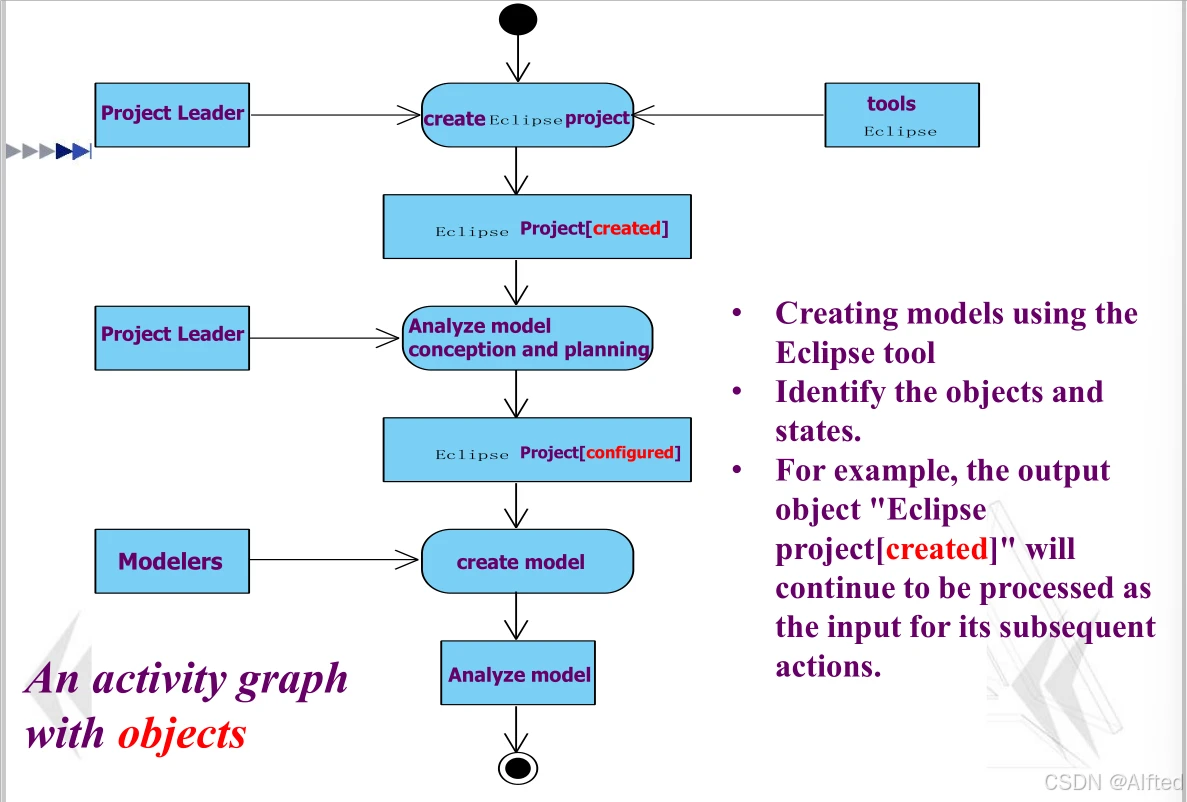
3.Swimlane-Role partition
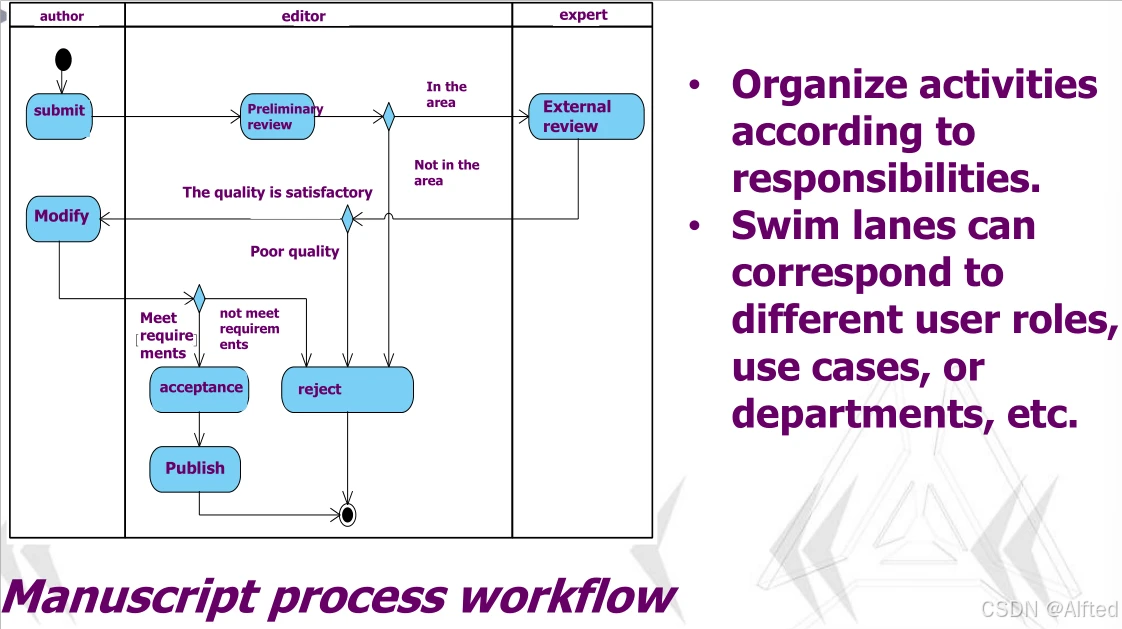
(7)Event Stream
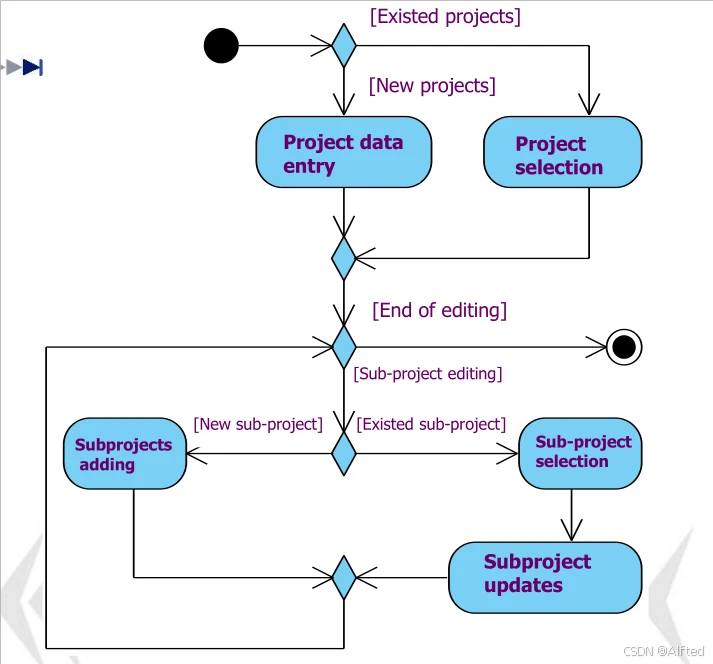
(8)Data flow
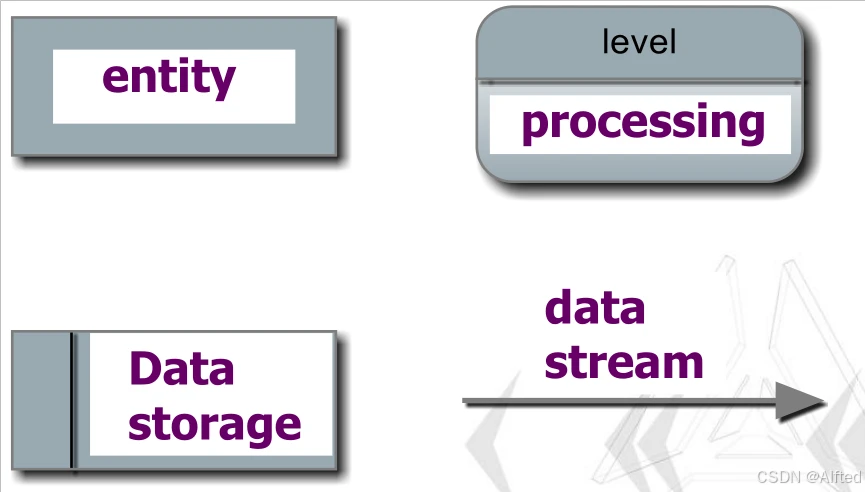
`·基本标志:Source or end point of data; Processing of transformed data; Data storage; Data flow.
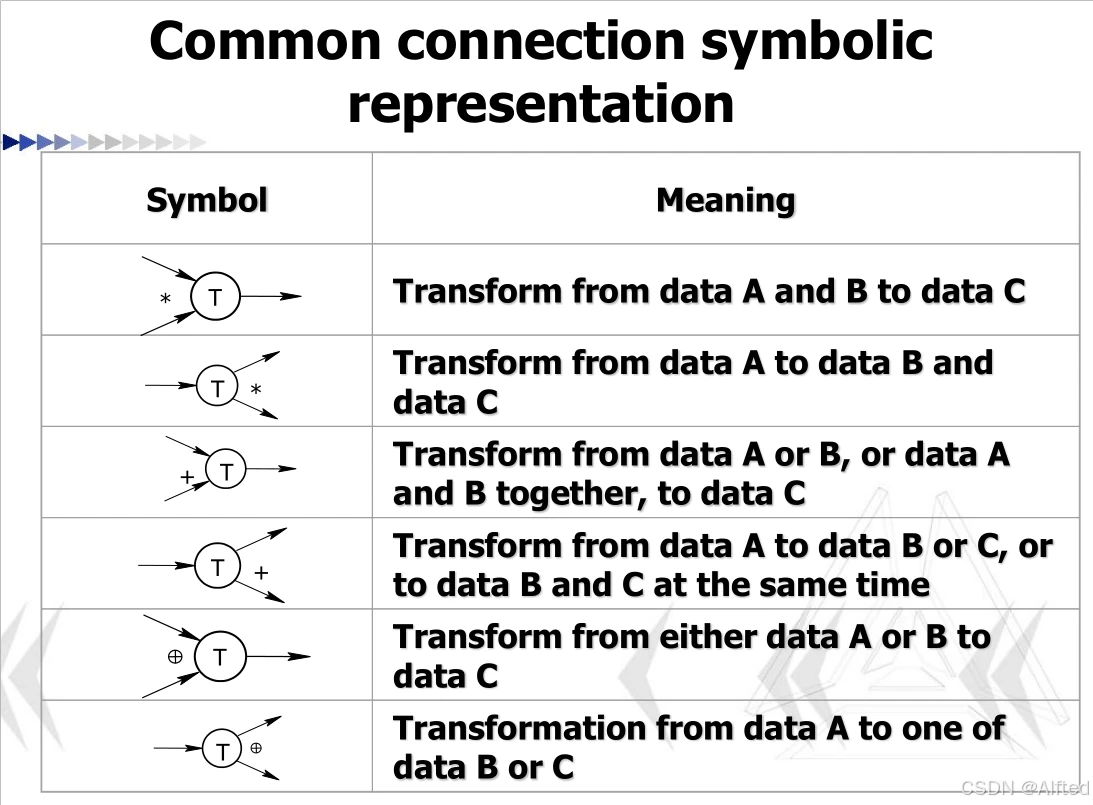
2.常见的连接符号
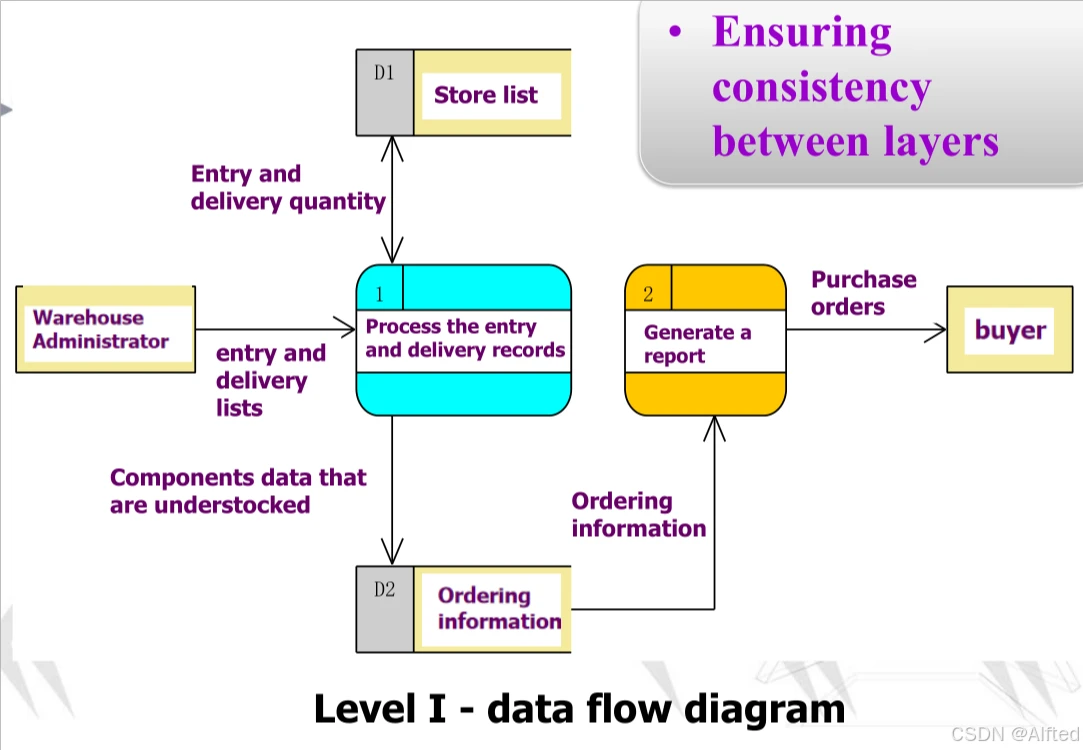
3.例子
(9)非功能性需求:质量需求;技术需要:硬件+软件平台+操作环境...
五、Systam architecture
~data和program/process组成的creation
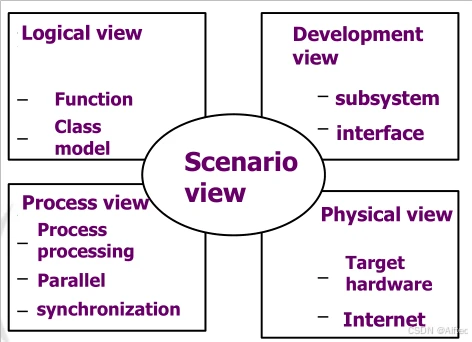
(1)“4+1”View Model
1.types:structural,framework, dynamic, process, functional
2.
(2)基本元素
1.Component:个再次使用的软件模板单元;表示主要的计算单元和数据存储
2.Connector: components间的交互
3.Configuration:components and connectors的拓扑逻辑和约束
(3)架构
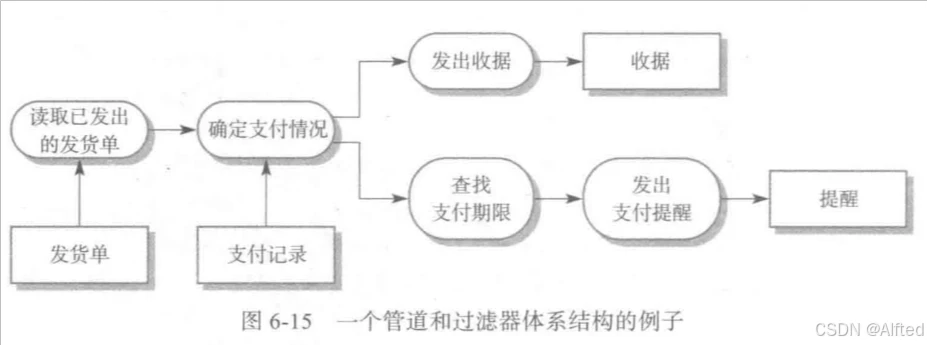
1.Pipe and filter
·filter间不能共享data
适用于用户交互很少的批处理系统和嵌入式系统
因为pipe-filter model需要处理数据流,而对于UI、复杂的输入/输出格式以及事件(如鼠标点击或菜单获取)的控制策略,很难将其转为可实现的数据流
例子:批处理应用
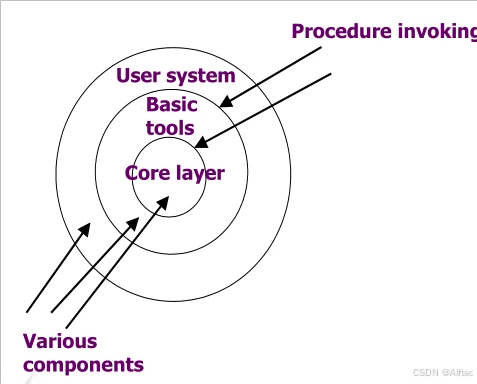
2.Multi-level system
·每一层都为上层服务
·Connectors间通过协议交换
·可以复杂化增量
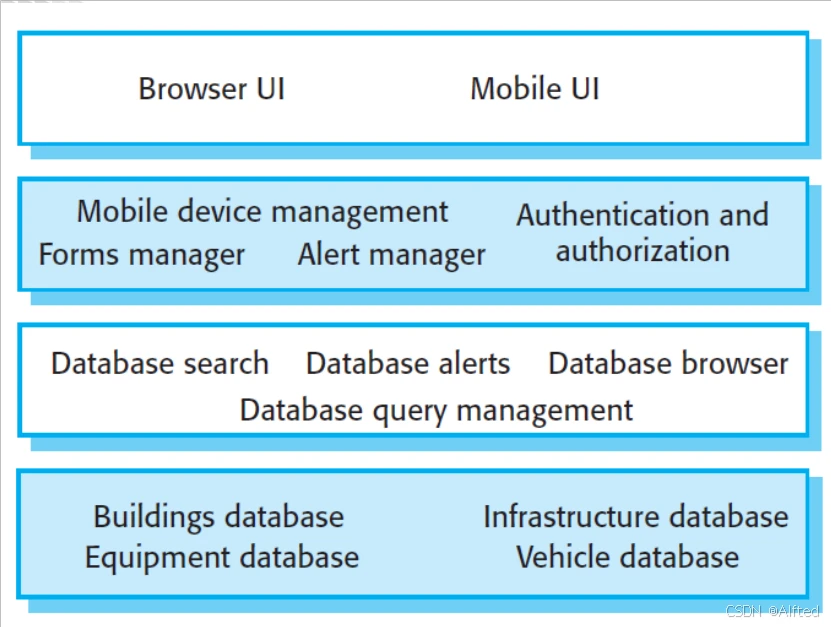
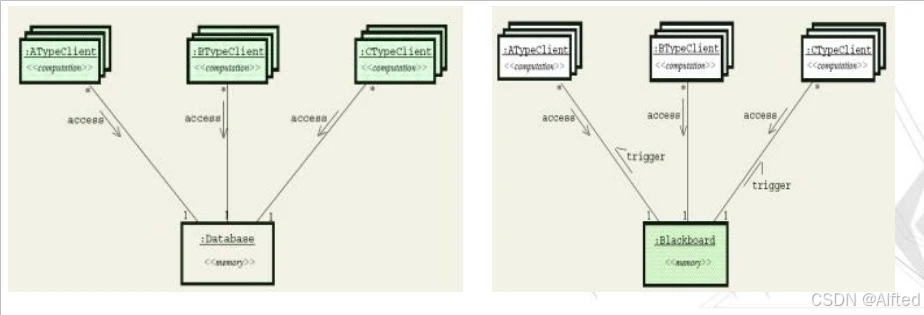
3.Warehouse系统
·components: Centraldata~和independent~
·event of the input stream->traditional database
·state of the central data structure->blackboard system
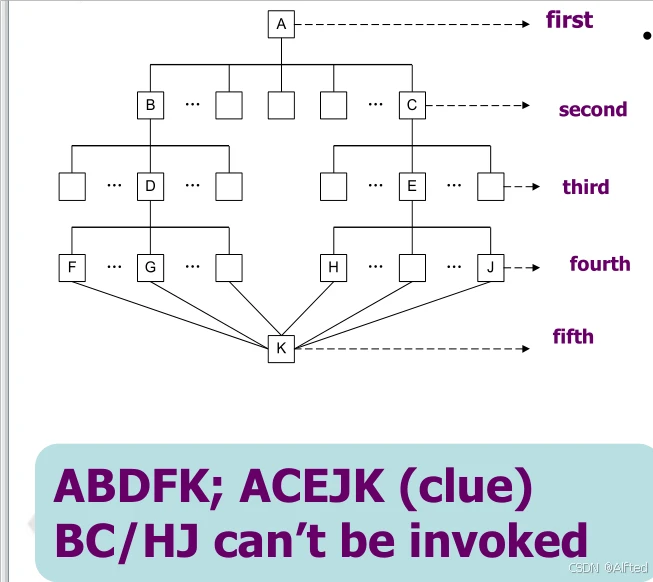
4.Orthogonal software architecture
·A layer is a set of components
·A clue is consisted of components with different functions.
5.Client/Server Architecture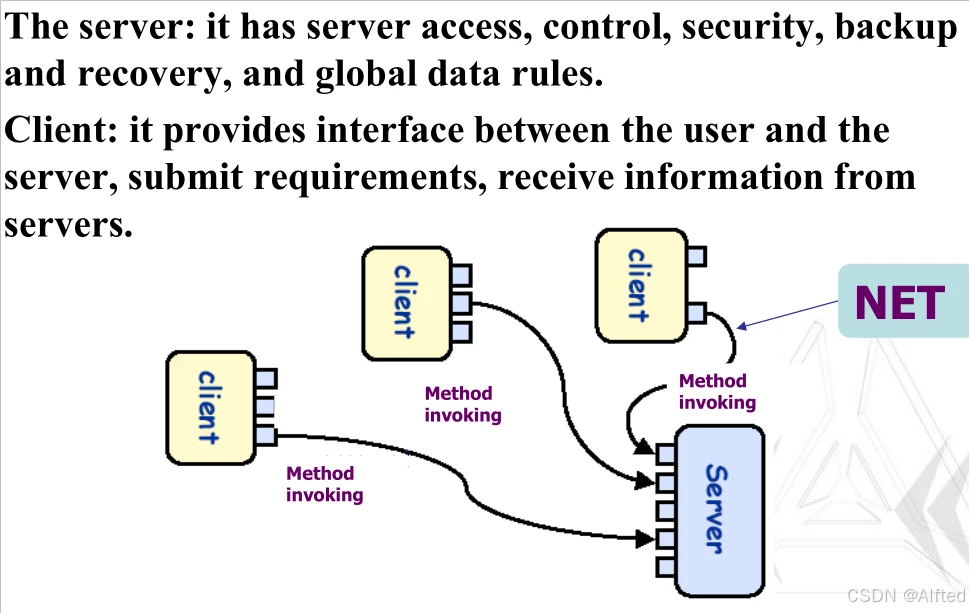
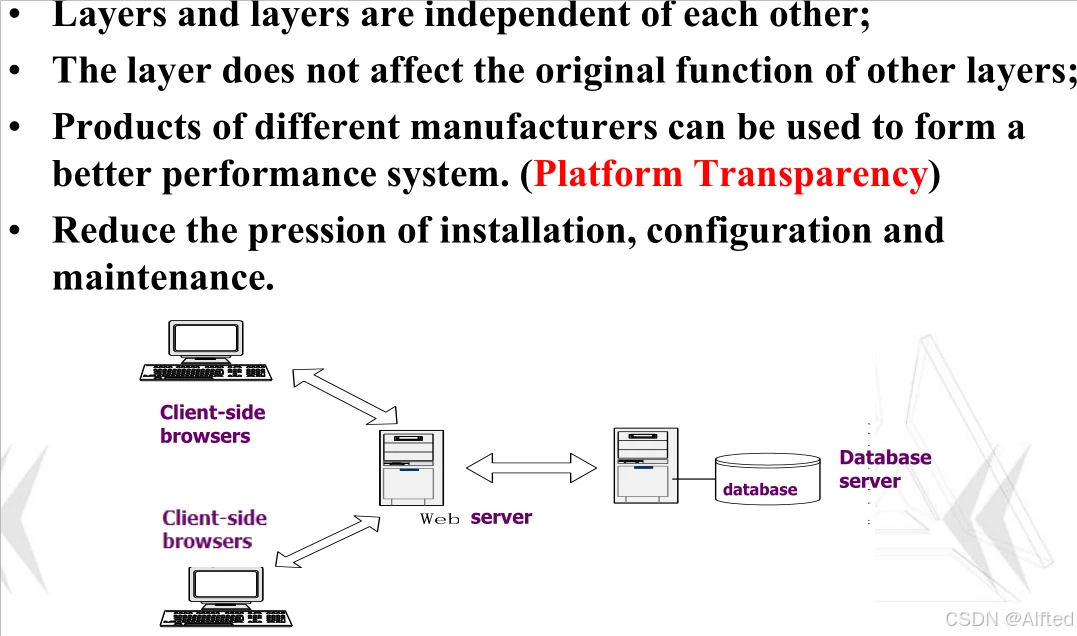
6.Browser/Server Architecture
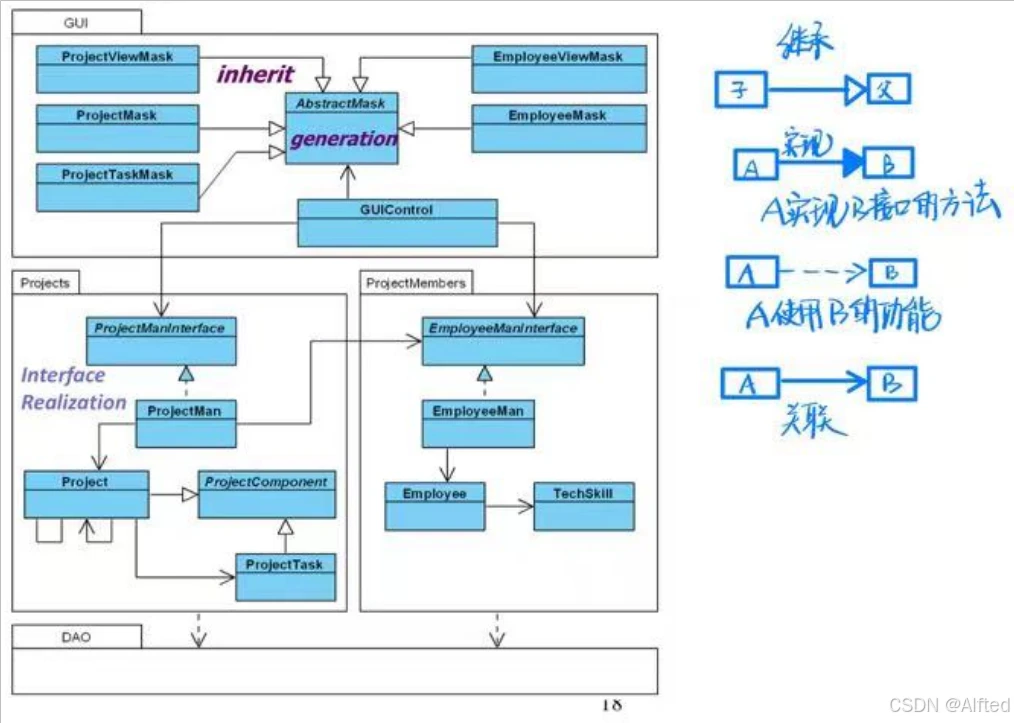
(4)Package
1.每个包都有个具体的功能,且独立
2.包之间没有循环依赖
到此这篇vb中名词解释(vb名词解释对象)的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关内容请继续浏览下面的相关推荐文章,希望大家都能在编程的领域有一番成就!
版权声明:
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若内容造成侵权、违法违规、事实不符,请将相关资料发送至xkadmin@xkablog.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即处理!
转载请注明出处,原文链接:https://www.xkablog.com/bcyy/13737.html
